Table of Contents
- Marketing Mix
- Marketing Mix Definition
- Elements of Marketing Mix
- Marketing Mix Modeling
- Marketing Mix Example
- What are the 4 C’s of Marketing?

Marketing Mix
Marketing: Identifying and Satisfying human & social needs profitably.
Mix: Two or more different qualities, things, or people, placed combined, or considered together.
The components of a product or service’s marketing plan are referred to as the marketing mix. Is a set of marketing tools that a firm uses to pursue its marketing objective in a target market.
Marketing Mix Definition
According to Neil H. Borden ‘ The Marketing mix is the set of marketing tools the firm uses to pursue its marketing objectives in the target market.’
- The collection of activities, or strategies, a business employs to sell its name or goods is known as the marketing mix
- The term “marketing mix” refers to the collection of various concepts and strategies that a marketing representative uses to support a specific brand or product.
- The marketing mix is the strategy that manufacturers use to succeed in the marketing domain.
Elements of Marketing Mix

For attracting consumers and providing them satisfaction, every manufacturer has to concentrate on four basic elements.
These are :
- Product
- Pricing
- Promotion
- Place (Distribution)
Product
A product is the core of marketing mix. When we talk about product we mean things like the quality of the product the design the packaging that’s sold in and the brand
Price
Price is the exchange value of a product i.e. the amount for which product is bought or sold. Price not only refers to the retail price but also any discounts you accept payment plans are there any specific credit terms that the consumer has to borrow money to buy your product.
Pricing decision is depend on
- Cost of Product,
- Objective of Marketer,
- Economic Condition,
- Competiton and so on.
Promotion
In today’s competitive market, there exist a number of brands with identical features. Promotion covers all forms of advertising, including emails, public relations, and personal selling by their sales representatives.
It then becomes necessary for an organization to actively promote its products.
Promotion mix includes :
- Advertising,
- Publicity,
- Sales Promotion,
- Salesmanship and so on.
Place (Distribution)
Another important aspect of marketing mix is place / physical distribution. The set of decisions related to physical distribution of goods and services from one place to another.
Place mix includes :
- Types of intermediaries available for distribution
- Channels of distribution
- Transportation, warehousing and inventory control for making product available to the consumers.
Marketing Mix Modeling
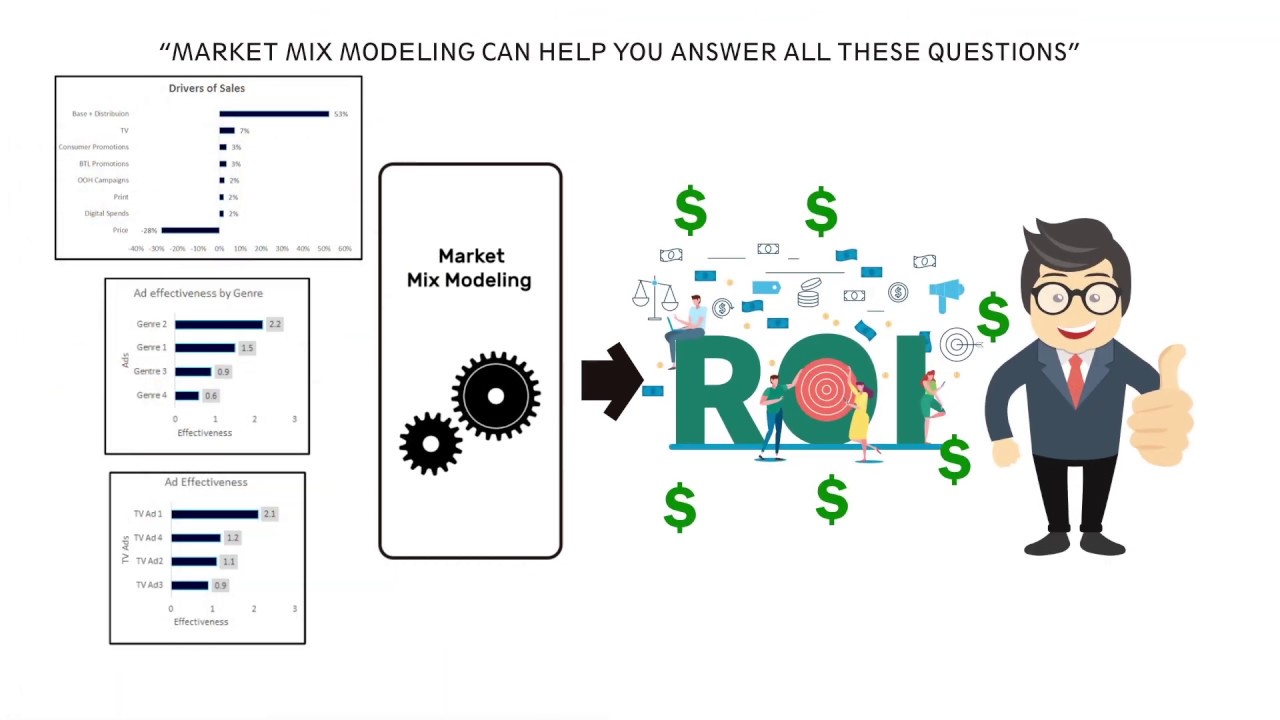
A highly resilient, privacy-friendly, data-driven statistical study, marketing mix modelling takes into account a variety of internal and external elements and attempts to determine how each of those factors separately and collectively impacts performance depending on your business, that could be sales or any kind of conversion.
Marketing mix modeling is also trying to understand the relative contribution of each variable on the outcome.
How Does Marketing Mix Modeling Work?

In essence, these models work by processing a lot of data for a lot of different variables and running them hundreds or thousands of times through a statistical model.
Where each model is trying to minimise the prediction error and maximise the business fit to reach an optimal one.
I’ve talked a little bit about the variables that can play a role here, but let’s categorise them. But a good exercise is to think about the importance variables for your business. Like what works for you.
we’ve baseline and seasonality, which includes – seasonlity & holidays
Media activities like TV, Print, outdoor, direct, display, search, social, and more .
External effects including – salary weeks, weather, consumer confidence index, and competitor activities.
And Internal effects like channel distribution activities, product changes, price changes, sales changes, sales process changes and organic content.
So depending which ones are relevant for your business, marketing mix models want data for all of those variables, which is fair enough.
The model then runs this data over and over again in different scenarios, under different conditions. With different weighting applied to minimise the prediction error and maximise the business fit to reach an optimal one.
The thing about MMM is that it’s flexible and you can constantly give it more information about your initiatives and the data you’re feeding into the model. Finally, from hundreds or thousands of models, it selects what it feels are the best representations of your marketing mix.
Why is MMM important for marketers?

Imapct can be easy to measure for some marketing initiatives, for others it’s more difficult. If we look at a modern marketing funnel, we know that people interact with your brand or your business in multiple places. Furthermore, people come and go from your ecosystem, sometimes being tracked and other times not, in the new era of privacy constraints.
The question of attribution has always been there, and in new age those questions become even more complex. This leaves marketers and data analysts asking the age old question. How important was each of those touch points to final sale?
With that said, it is becoming increasingly difficult to track people’s interactions with your brand or business across the internet. This makes the job of a marketer much more difficult.
A marketer now needs to get a holistic understanding of the channel mix and how they can pull on different levers at different times to positively affect performance. With tracking getting increasingly more difficult, this understanding comes in the form of aggregated data, sliced and diced in different ways so you can create impactful hypotheses to test.
Hypothesoize, test, and learn.
What I’m saying is that it’s important now for modern marketers to have as much information as possible to base their decisions on.
MMM isn’t an attribution tool.
It isn’t the answer to the changing privacy landscape, but it will help you give more information about your past and future performance.
How can MMM be used?

As I said, MMM provides more information on which to make decisions. There are lots of applications, but let us outline three common ones.
- ROI analysis
The most common application is to understand the return on investment from different marketing and sales channels. This gives the marketer more of an understanding of what drives performance.
- Forecasting
Another common use for MMM is for forecasting and projecting budgets and spends.
Think about it I large businesses so many teams need to know what marketing spending will look like weeks or even months ahead.
And although MMM doesn’t provide exact forecasts, the output can be used to predict roughly what spends and outcomes will be.
So other parts of the business can plan accordingly.
- Pricing
What you’re essentially trying to understand is how would altering prices alter the outcome. This is, of course, an incredibly complex question, but with the right data and right model it can help but pieces of that puzzle together so you can make pricing decisions and understand how to market might react.
Marketing Mix Example

Let’s say you want to sell hamburgers great but first you need to know your target market who are you going to sell hamburgers to well I know that your target market will affect your four p’s in this case you’ll want a very high-end hamburger consider a product that features truffle which are super expensive stinky mushrooms hey that sounds delightful Due to your high cost of $25, you will need to charge a lot. A excellent advertisement in a fancy-oants magazine could be a terrific way to promote a product place to sell the hamburger would be at the Polo Club okay….
but what if we have a different target market what about this guy please man this marketing mix won’t labour for him Think about serving him a vegetarian burger; you probably won’t be able to charge much and might even need to give him a loan. If you give him some fries, it will be motivating for him to spread the word and selling them in a public park would be a good idea okay…..
but what about this target market our rule again we should adapt the marketing mix he spends a lot of time at sees the waterproof packaging would be a good idea. he doesn’t have any cash but has plenty of goats on board and who doesn’t love a free viking helment wool you’ll need to deliver.
The marketing mix is comprised of four key elements: product, pricing, promotion, and place.
What are the 4 C’s of Marketing?

- Why does it make sense to replace the letter “P” with a letter “C” in marketing ?
- What does Marketing Mix mean for the client and how to plan the organization’s activities according to its principles?
- In what ways is 4C related to the classic 4P concept and why is it only the combination of both that can give us the best results?
The classic 4P marketing product, price, place, and promotion has been the foundation of marketing strategies for many years over time as the service sector had grown 4P expanded to 7P introducing people, processes, and physical evidence. However, it’s worth observing that both 4P and 7P concepts evaluate marketing instruments from the point of view of the company and not the customer that’s why in 1990 Robert Lauterborn developed 4C marketing which included the same elements as the classic 4P but seen from the consumer’s point of view.
The 4C marketing model consists of the following elements :
Customer (product): The customer’s needs motivations and goals that are of the greatest interest to the marketer. The marketer’s task is to discover them which requires a shift of emphasis to marketing research therefore, the product from the 4P concept becomes less important than conducting research in the market.
Cost (price): It is a price for a product or service but seen from the customer’s perspective as a cost they have to buy in order to make a purchase notice a sum of money the company will earn. Moreover, here the term cost covers much more than just the financial aspect it is also the time that the customer has to spend on purchasing transporting ordering goods online or any risks that the transaction may entail
Convenience (pace): It is about looking at the aspects of product distribution through the eyes of the clients aiming to make a given product or service available for them in the most convenient place in time it also means giving the clients easy-to-access information about the product for example on a well-functioning website in catalogues or on social media.
Communication (promotion): This model stands for communication which is the equivalent of promotion in the 4p concept in 4c marketing the company shifts the emphasis from merely informing clients about the product to building a deeper relationship with them via communication activities this is achieved by maintaining activity on social media content marketing or various activity that create the customer experience.
